There are two types of properties for every matter physical property and chemical property. Today you will get a brief idea of the physical properties of matter.
So today we are going to discuss the physical properties of matter.
If you are looking for physical properties definitions, this will be the ultimate guide and ready reference for you.
What is physical property?
Physical properties are those property which can be measure by its appearance without changing chemical identity.
In short physical property might have been involved physical change but not in a chemical change.
If the chemical change occurs the observed characteristics are a chemical property.
1. Intensive property:
It is a property that depends on the type of matter in a sample, not on amount of matter.
2. Extensive property:
It is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample.
List of physical properties and chemical properties:
- Description
- Identification
- Sampling
- GRN
- A.R.No.
- pH
- Solubility
- Conductivity
- Heavy metal
- Loss on drying
- Residue on ignition
- Loss on ignition
- Sulphated ash
- Ash content
- Melting point
- Boiling point
- Freezing point
- Density
- Bulk density
- Tap density
- Specific gravity
- Viscosity
- Water content
- Particle size
- Limit test
- Specific optical rotation
- Refractive index
- Acidity
- Alkalinity
- Residual solvent
Definitions of physical properties:
 |
| Description |
Que: What is Identification?
Ans: Identification is a test to perform for proving the drug substance identity by using different techniques like UV, IR, TLC, HPLC etc.
Que: Definition of sampling?
Ans: Sampling is processed to withdraw a smaller portion of the sample as representative of the whole batch for analysis.
Que: What is GRN?
Ans: It is a good-received note for any drug substance which is received by the organisation as an intimation.
Que: What is A.R.No?
Ans: It is an in-house reference number given to the sample for easy identification.
Que: Definition of pH?
Ans: pH is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration present in the solution.
Que: Definition of Solubility?
Ans: Solubility is a test to check the sample’s ability to dissolve in a solvent.
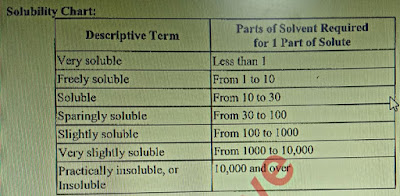 |
| Solubility chart |
Que: Definition of Conductivity?
Ans: Conductivity is the ability of a sample to conduct electricity.
Que: Definition of Heavy metal?
Ans: It is a test to measure the level of harmful metals present in the sample.
Que: Definition of Loss on drying?
Ans: It is a loss of weight of the sample after drying on a specified condition.
Que: Definition of Residue on ignition?
Ans: It is a leftover residue of the sample on ignition.
Que: Definition of Loss on Ignition?
Ans: It is the same as loss in drying only performed at high temperatures.
Que: Definition of sulphates ash?
Ans: Sulphates ash is a left-out incombustible material present in the sample after being burned.
Que: Definition of Ash content?
Ans: Refer to sulphated ash.
Que: Definition of a melting point?
Ans: It is a temperature at which a given solid start to melt.
Que: Definition of a boiling point?
Ans: It is the temperature at which a given liquid start to boil.
Que: Definition of a freezing point?
Ans: It is a temperature at which a given liquid start to freeze.
Que: Definition of Density?
Ans: Density is a quantity of a mass of a sample per unit volume.
D=m/v
where D is the density
m is mass,
v is volume
Que: Definition of Bulk density?
Ans: It is an untapped volume of a mass of a sample.
Que: Definition of Tap density?
Ans: It is a tapped volume of a mass of a sample.
Que: Definition of specific gravity?
Ans: It is a ratio of a density of a sample to the density of a standard.
It is also known as relative density
Que: Definition of viscosity?
Ans: Viscosity is resistance to the flow of liquid.
Que: Definition of water content?
Ans: Water content is nothing but moisture present in a sample.
Que: Definition of particle size?
Ans: It is a test to determine the size of the particle which is present in the sample.
Que: Definition of a limit test?
Ans: The limit test is defined as a quantitative or semi-quantitative test designed to identify and control small impurities which are likely to be present in a substance.
Que: Definition of specific optical rotation?
Ans: Specific Optical rotation of a substance is an angle of rotation when plane-polarized light passed through it.
Que: Definition of the refractive index?
Ans: Refractive index is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium.
Que: Definition of acidity?
Ans: Acidity is the level of acid in a substance.
Que: Definition of alkalinity?
Ans: Alkalinity is a measure of the capacity to neutralize the acid.
Que: Definition of residual solvent?
Ans: Residual solvent is defined as the organic volatile chemicals that are used or produced in the manufacturing of a drug substance or excipient or drug product.
Also read: Infrared spectroscopy
- HPLC Calibration Parameters in pharma
- How to Do Calibration of FTIR Spectrophotometer?
- HPLC Interview Question and Answers
- QC Interview Questions & Answers
Refer YT Channel: Pharmabeejpro


Comments are closed.